Introduction
Rapid T cell reconstitution following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is essential for protection against infections and has been associated with lower incidence of chronic graft-vs-host disease (cGVHD), relapse and transplant-related mortality (TRM). While cord blood (CB) transplants are associated with lower rates of cGVHD and relapse, their low stem cell content results in slower immune reconstitution and higher risk of graft failure, severe infections and TRM. Recently, results of a Phase I/II trial revealed that single UM171-expanded CB transplant allowed the use of smaller CB units without compromising engraftment. We now report on T cell reconstitution and immune function in patients transplanted with UM171-expanded CB grafts.
Methods
We performed a retrospective analysis of 20 patients treated with UM171-expanded CB and compared it to a contemporary cohort of 12 patients treated in the same institution who received unmanipulated CB transplant with similar conditioning regimens. Of note, no patient received ATG as part of the conditioning in either cohort. We used flow cytometry and TCR sequencing to evaluate T cell reconstitution, and virus-specific ELISpot assays to evaluate T cell function in the first year post-transplantation. We also categorized infectious events as per definitions of infection severity in the BMT CTN Technical MOP Version 3.0 and report the mean cumulative count of infectious events for each cohort.
Results
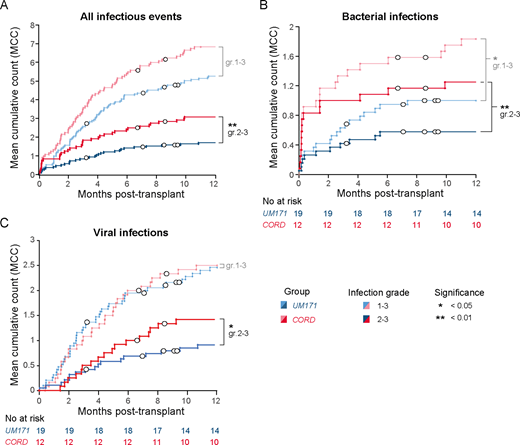
While median T cell dose in graft was at least 2-3x lower for the cohort of patients treated with UM171-expanded CB due to the selection of smaller cords and to cell loss occurring during CD34 selection process, numbers and phenotype of T cells at 3, 6 and 12 months post-transplant were similar in patients treated with UM171-expanded or unmanipulated CB transplant. TCR sequencing analyses revealed that UM171 patients had greater T cell diversity and higher numbers of T cell clonotypes at 12 months post-transplant compared to patients who received unmanipulated CB. Younger UM171 patients (i.e. <40 years old) also showed a more pronounced increase in naïve T cells and recent thymic emigrants (RTE) between 3- and 12-months post-transplant compared to age-matched unmanipulated CB patients, suggesting that UM171-expansion improves thymopoiesis at least in the young patients. This also correlated with the demonstration that UM171 expands common lymphoid progenitors in vitro. ELISpot assays revealed that UM171 patients showed early virus-specific T cell reactivity, at 2- and 3-months post-transplant. Most importantly, UM171 patients had a 2-fold lower frequency of severe (i.e. grade 2-3) infections at 1 year post-transplant, even though time to engraftment of 500 neutrophils was similar between the two cohorts (17 and 20 days for the UM171-expanded and unmanipulated CB cohorts respectively, p=0.94).
Conclusion
Our data show that the relative T-cell paucity of the UM171 graft is rapidly compensated after transplant with no significant difference observed between the two cohorts in terms of numbers and phenotypes of T cells at 3, 6 or 12 months post-transplant. Although it is difficult to dissect the relative contribution of homeostatic expansion and de novo thymopoiesis, recipients of UM171 grafts had a greater TCR diversity at one year, which was more evident among patients younger than 40 years of age. The prompt immune reconstitution observed in UM171 patients translated into a low rate of severe (grade 2-3) infections and no infection-related mortality. These results support rapid and functional T cell reconstitution following UM171 expanded CB transplantation, which likely contributes to the absence of moderate/severe cGVHD, infection-related mortality and late TRM observed in this cohort.
Figure legend: Mean cumulative counts of infectious events in patients transplanted with UM171-expanded (blue) or unmanipulated (red) CB. Mean cumulative counts are shown for all infectious events (A), bacterial (B) and viral (C) infections. Events were categorized by type and severity as per BMT CTN guidelines (Appendix 4A). Infectious events of grade 1-3 are shown in pale colors, while more severe events (grade 2-3) are shown in dark colors. Censored patients (including those who relapsed) are indicated with white circles.
Dumont-Lagacé:ExCellThera: Current Employment. Busque:Novartis: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria. Sauvageau:ExCellThera: Current equity holder in private company, Other: CEO, Patents & Royalties. Cohen:ExCellThera: Consultancy, Other: principal investigator of an ongoing UM171 clinical trial.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal